[Avg. reading time: 9 minutes]
CAP Theorem
 src 1
src 1
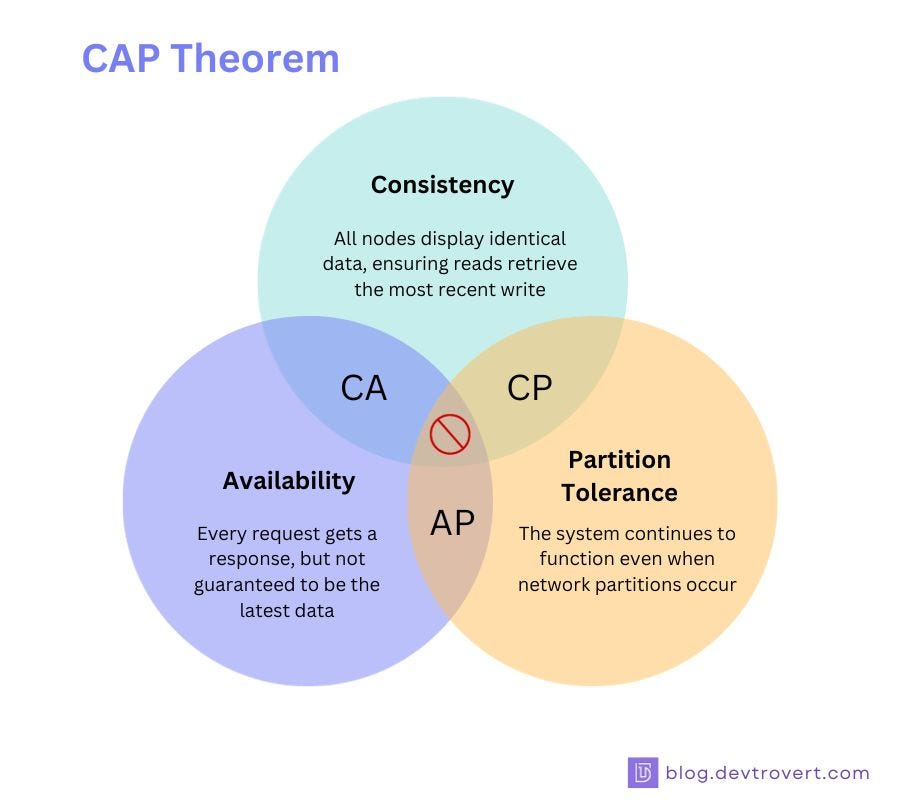
The CAP Theorem is a fundamental concept in distributed computing. It states that in the presence of a network partition, a distributed system can guarantee only two out of the following three properties:
The Three Components
-
Consistency (C)
Every read receives the most recent write or an error.
Example: If a book’s location is updated in a library system, everyone querying the catalog should see the updated location immediately. -
Availability (A)
Every request receives a (non-error) response, but not necessarily the most recent data.
Example: Like a convenience store that’s always open, even if they occasionally run out of your favorite snack. -
Partition Tolerance (P)
The system continues to function despite network failures or communication breakdowns.
Example: A distributed team in different rooms that still works, even if their intercom fails.
What the CAP Theorem Means
You can only pick two out of three:
| Guarantee Combination | Sacrificed Property | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
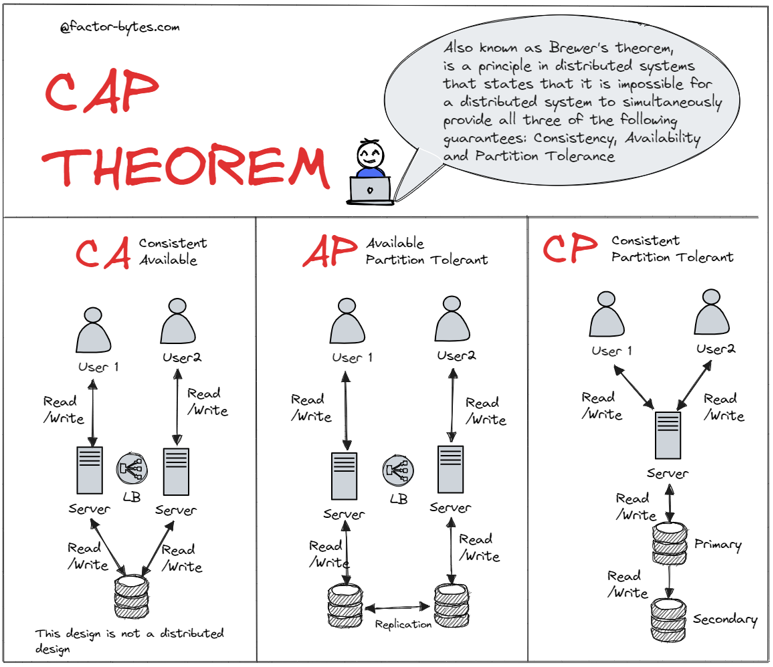
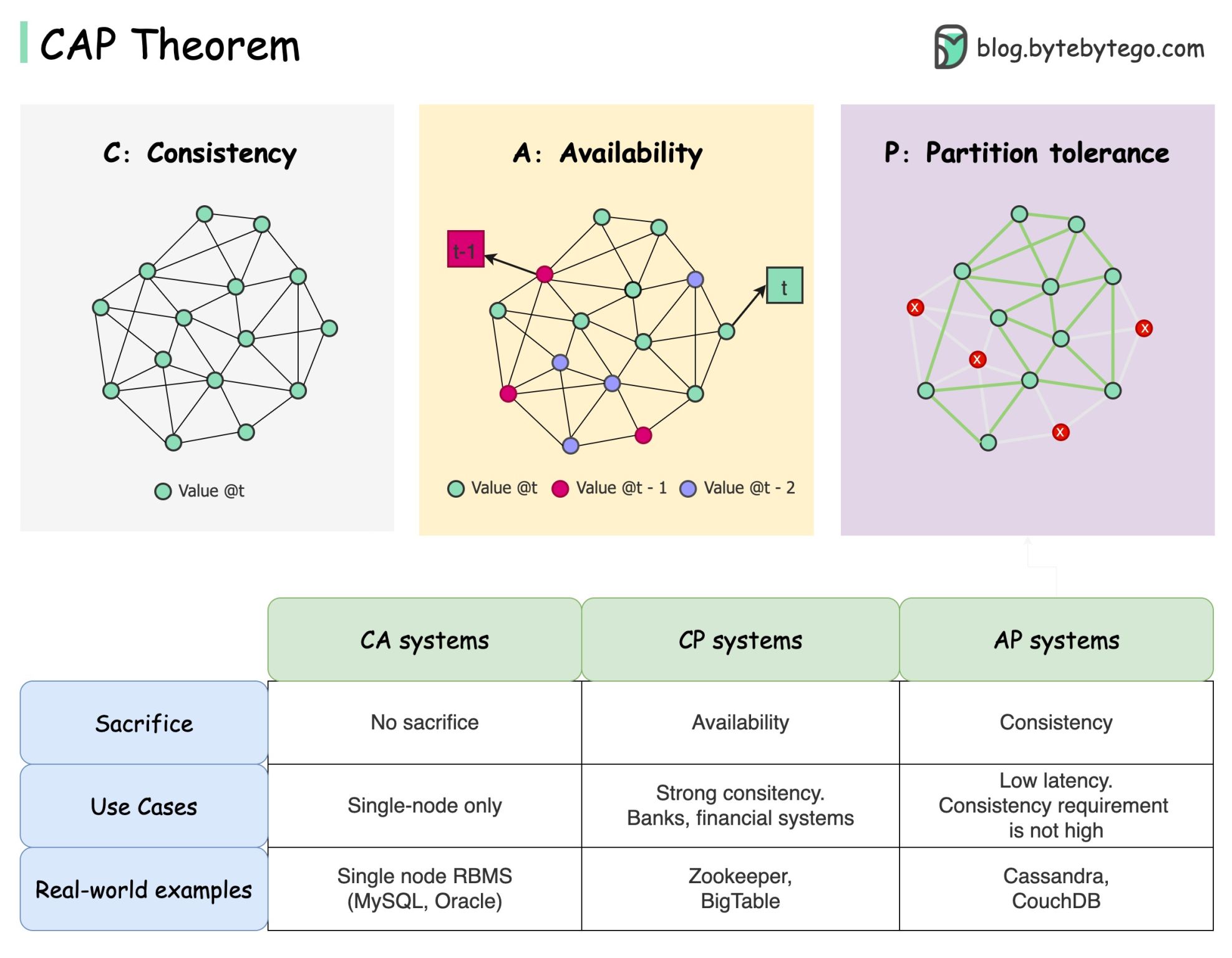
| CP (Consistency + Partition) | Availability | Banking Systems, RDBMS |
| AP (Availability + Partition) | Consistency | DNS, Web Caches |
| CA (Consistency + Availability) | Partition Tolerance (Not realistic in distributed systems) | Only feasible in non-distributed systems |
 src 2
src 2
Real-World Examples
CAP Theorem trade-offs can be seen in:
- Social Media Platforms – Favor availability and partition tolerance (AP)
- Financial Systems – Require consistency and partition tolerance (CP)
- IoT Networks – Often prioritize availability and partition tolerance (AP)
- eCommerce Platforms – Mix of AP and CP depending on the service
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) – Strongly AP-focused for high availability and responsiveness
 src 3
src 3
graph TD
A[Consistency]
B[Availability]
C[Partition Tolerance]
A -- CP System --> C
B -- AP System --> C
A -- CA System --> B
subgraph CAP Triangle
A
B
C
end
This diagram shows that you can choose only two at a time:
- CP (Consistency + Partition Tolerance): e.g., traditional databases
- AP (Availability + Partition Tolerance): e.g., DNS, Cassandra
- CA is only theoretical in a distributed environment (it fails when partition occurs)
In distributed systems, network partitions are unavoidable. The CAP Theorem helps us choose which trade-off makes the most sense for our use case.
#cap #consistency #availability #partitiontolerant
1: blog.devtrovert.com
2: Factor-bytes.com
3: blog.bytebytego.com