[Avg. reading time: 20 minutes]
Parquet
Parquet is a columnar storage file format optimized for use with Apache Hadoop and related big data processing frameworks. Originally developed by Twitter and Cloudera, Parquet provides a compact and efficient way of storing large, flat datasets.
Best suited for WORM (Write Once, Read Many) workloads.
Row Storage
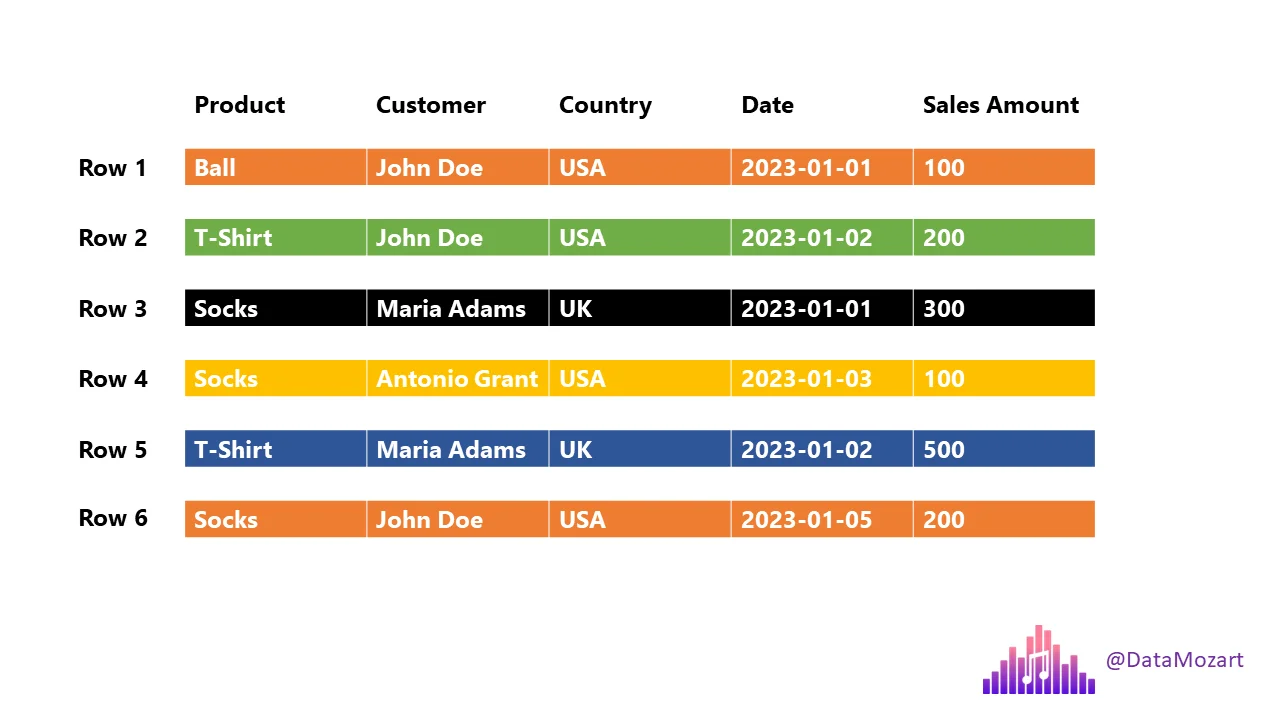
Give me list of Total T-Shirts sold or Customers from UK
It scans the entire dataset.
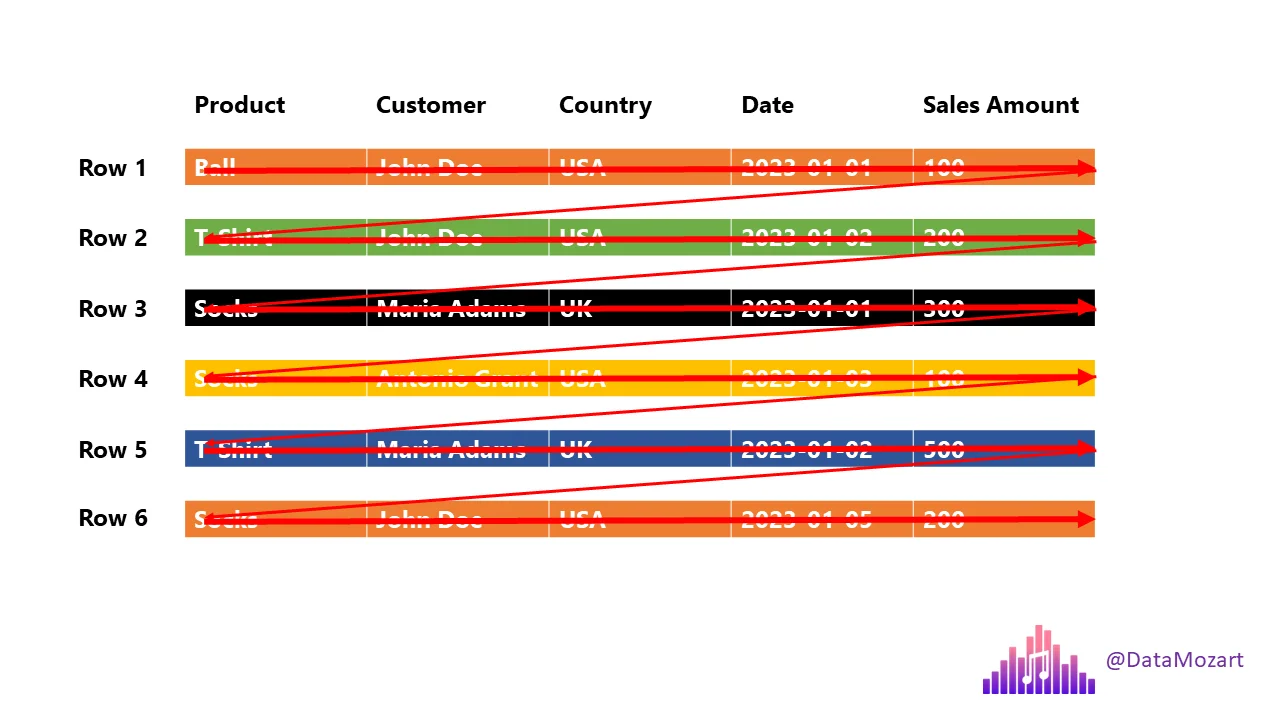
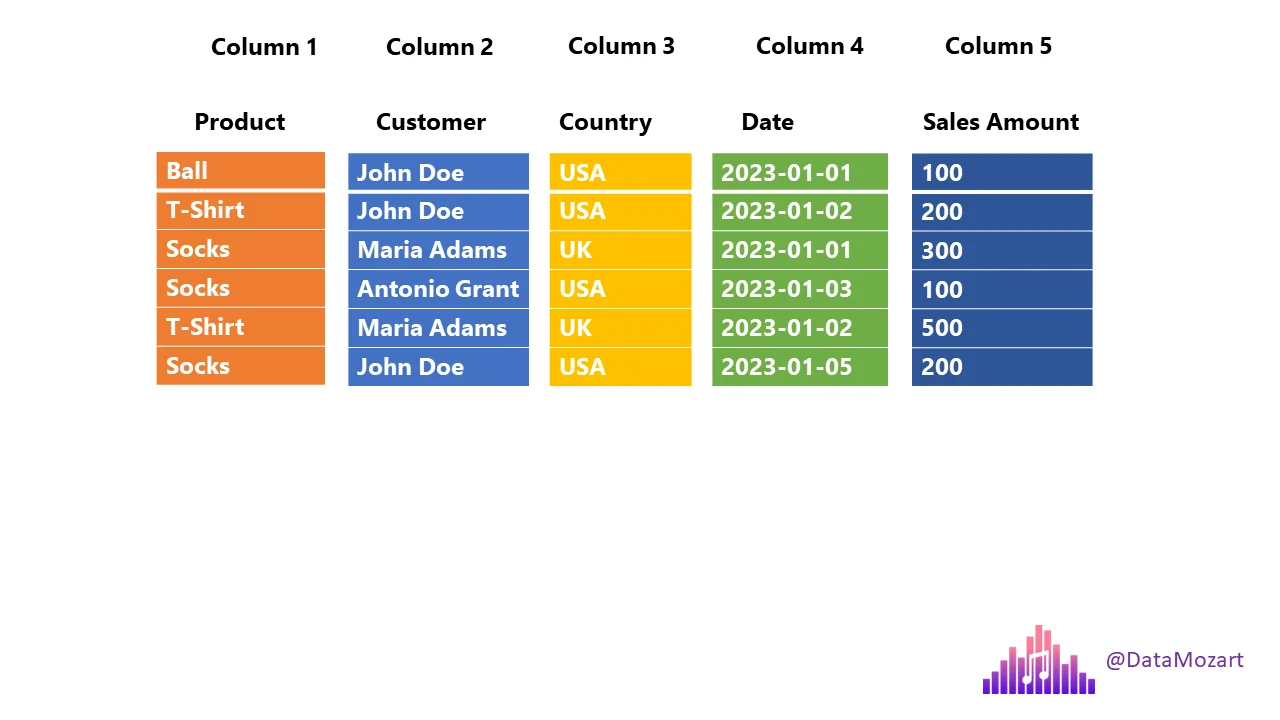
Columnar Storage
Terms to Know
Projection: Columns that are needed by the query.
select product, country, salesamount from sales;
Here the projections are: product, country & salesamount
Predicate: A filter condition that selects rows.
select product, country, salesamount from sales where country='UK';
Here predicate is where country = 'UK'
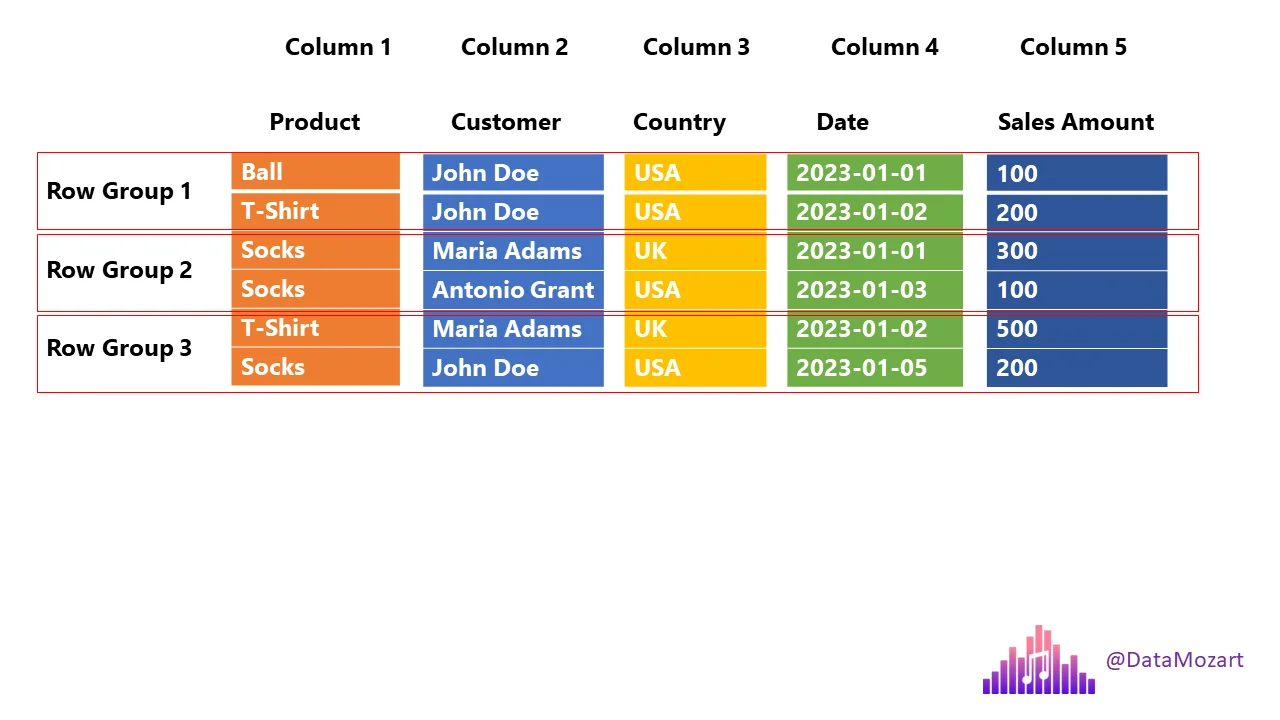
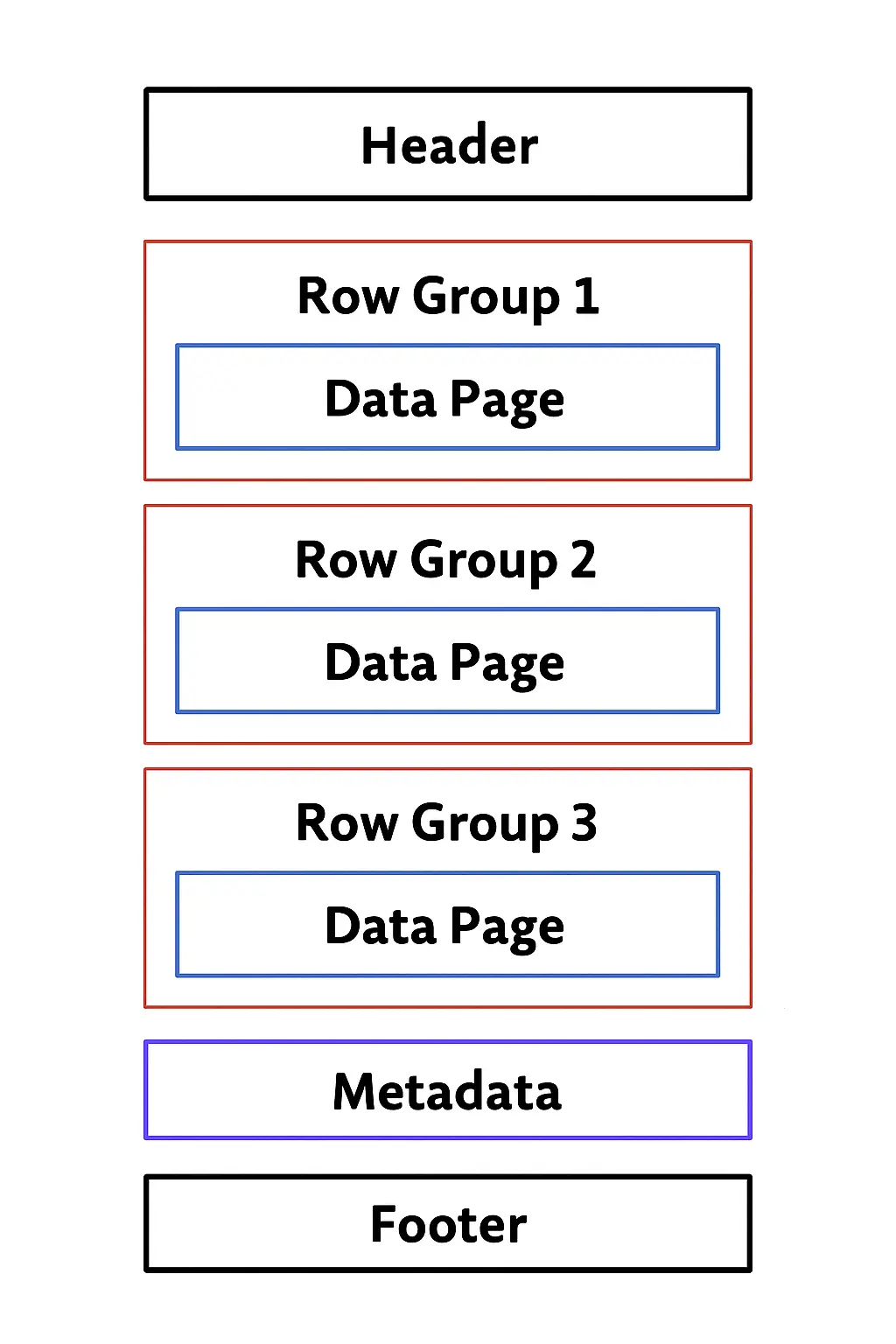
Row Groups in Parquet
-
Parquet divides data into row groups, each containing column chunks for all columns.
-
Horizontal partition—each row group can be processed independently.
-
Row groups enable parallel processing and make it possible to skip unnecessary data using metadata.
Parquet - Columnar Storage + Row Groups
Parquet File format
Parquet Fileformat Layout {{footnote: https://parquet.apache.org/docs/file-format/}}
Sample Data
| Product | Customer | Country | Date | Sales Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball | John Doe | USA | 2023-01-01 | 100 |
| T-Shirt | John Doe | USA | 2023-01-02 | 200 |
| Socks | Jane Doe | UK | 2023-01-03 | 150 |
| Socks | Jane Doe | UK | 2023-01-04 | 180 |
| T-Shirt | Alex | USA | 2023-01-05 | 120 |
| Socks | Alex | USA | 2023-01-06 | 220 |
Data stored inside Parquet
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ File Header │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Magic Number: "PAR1" │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
├──────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Row Group 1 │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Column Chunk: Product │ │
│ │ ├─ Page 1: Ball, T-Shirt, Socks │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Column Chunk: Customer │ │
│ │ ├─ Page 1: John Doe, John Doe, Jane Doe│ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Column Chunk: Country │ │
│ │ ├─ Page 1: USA, USA, UK │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Column Chunk: Date │ │
│ │ ├─ Page 1: 2023-01-01, 2023-01-02, │ │
│ │ 2023-01-03 │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Column Chunk: Sales Amount │ │
│ │ ├─ Page 1: 100, 200, 150 │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Row Group Metadata │ │
│ │ ├─ Num Rows: 3 │ │
│ │ ├─ Min/Max per Column: │ │
│ │ • Product: Ball/T-Shirt/Socks │ │
│ │ • Customer: Jane Doe/John Doe │ │
│ │ • Country: UK/USA │ │
│ │ • Date: 2023-01-01 to 2023-01-03 │ │
│ │ • Sales Amount: 100 to 200 │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
├──────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Row Group 2 │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Column Chunk: Product │ │
│ │ ├─ Page 1: Socks, T-Shirt, Socks │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Column Chunk: Customer │ │
│ │ ├─ Page 1: Jane Doe, Alex, Alex │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Column Chunk: Country │ │
│ │ ├─ Page 1: UK, USA, USA │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Column Chunk: Date │ │
│ │ ├─ Page 1: 2023-01-04, 2023-01-05, │ │
│ │ 2023-01-06 │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Column Chunk: Sales Amount │ │
│ │ ├─ Page 1: 180, 120, 220 │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Row Group Metadata │ │
│ │ ├─ Num Rows: 3 │ │
│ │ ├─ Min/Max per Column: │ │
│ │ • Product: Socks/T-Shirt │ │
│ │ • Customer: Alex/Jane Doe │ │
│ │ • Country: UK/USA │ │
│ │ • Date: 2023-01-04 to 2023-01-06 │ │
│ │ • Sales Amount: 120 to 220 │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
├──────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ File Metadata │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Schema: │ │
│ │ • Product: string │ │
│ │ • Customer: string │ │
│ │ • Country: string │ │
│ │ • Date: date │ │
│ │ • Sales Amount: double │ │
│ ├────────────────────────────────────────┤ │
│ │ Compression Codec: Snappy │ │
│ ├────────────────────────────────────────┤ │
│ │ Num Row Groups: 2 │ │
│ ├────────────────────────────────────────┤ │
│ │ Offsets to Row Groups │ │
│ │ • Row Group 1: offset 128 │ │
│ │ • Row Group 2: offset 1024 │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
├──────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ File Footer │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Offset to File Metadata: 2048 │ │
│ │ Magic Number: "PAR1" │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────┘
PAR1 - A 4-byte string "PAR1" indicating this is a Parquet file.
The type of compression used (e.g., Snappy).
Snappy
- Low CPU Util
- Low Compression Rate
- Splittable
- Use Case: Hot Layer
- Compute Intensive
GZip
- High CPU Util
- High Compression Rate
- Splittable
- Use Case: Cold Layer
- Storage Intensive
Encoding
Encoding is the process of converting data into a different format to:
- Save space (compression)
- Enable efficient processing
- Support interoperability between systems
Packing clothes and necessities in a luggage vs organizing them in separate sections for easier retrieval.
Plain Encoding
- Stores raw values as-is (row-by-row, then column-by-column).
- Default for columns that don’t compress well or have high cardinality (too many unique values,ex id/email). Ex: Sales Amount
Dictionary Encoding
-
Stores a dictionary of unique values and then stores references (indexes) to those values in the data pages.
-
Great for columns with repeated values.
Example:
- 0: Ball
- 1: T-Shirt
- 2: Socks
- Data Page: [0,1,2,2,1,2]
Reduces storage for repetitive values like "Socks".
Run-Length Encoding (RLE)
-
Compresses consecutive repeated values into a count + value pair.
-
Ideal when the data is sorted or has runs of the same value.
Example:
If Country column was sorted: [USA, USA, USA, UK, UK, UK]
RLE: [(3, USA), (3, UK)]
- Efficient storage for sorted or grouped data.
Delta Encoding
-
Stores the difference between consecutive values.
-
Best for numeric columns with increasing or sorted values (like dates).
Example:
Date column: [2023-01-01, 2023-01-02, 2023-01-03, ...]
Delta Encoding: [2023-01-01, +1, +1, +1, ...]
- Very compact for sequential data.
Bit Packing
-
Packs small integers using only the bits needed rather than a full byte.
-
Often used with dictionary-encoded indexes.
Example:
Dictionary indexes for Product: [0,1,2,2,1,2]
Needs only 2 bits to represent values (00, 01, 10).
Saves space vs. storing full integers.
Key Features of Parquet
Columnar Storage
Schema Evolution
- Supports complex nested data structures (arrays, maps, structs).
- Allows the schema to evolve over time, making it highly flexible for changing data models.
Compression
-
Parquet allows the use of highly efficient compression algorithms like Snappy and Gzip.
-
Columnar layout improves compression by grouping similar data together—leading to significant storage savings.
Various Encodings
Language Agnostic
- Parquet is built from the ground up for cross-language compatibility.
- Official libraries exist for Java, C++, Python, and many other languages—making it easy to integrate with diverse tech stacks.
Seamless Integration
-
Designed to integrate smoothly with a wide range of big data frameworks, including:
- Apache Hadoop
- Apache Spark
- Amazon Glue/Athena
- Clickhouse
- DuckDB
- Snowflake
- and many more.
Python Example
import pandas as pd
file_path = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gchandra10/filestorage/main/sales_100.csv'
# Read the CSV file
df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
# Display the first few rows of the DataFrame
print(df.head())
# Write DataFrame to a Parquet file
df.to_parquet('sample.parquet')
Some utilities to inspect Parquet files
WIN/MAC
https://aloneguid.github.io/parquet-dotnet/parquet-floor.html#installing
MAC
https://github.com/hangxie/parquet-tools
parquet-tools row-count sample.parquet
parquet-tools schema sample.parquet
parquet-tools cat sample.parquet
parquet-tools meta sample.parquet
Remote Files
parquet-tools row-count https://github.com/gchandra10/filestorage/raw/refs/heads/main/sales_onemillion.parquet