[Avg. reading time: 4 minutes]
Azure Cloud
Servers: Individual Machines
Data Centers: These are the physical buildings that house servers and other components like networking, storage, and compute resources
Availability Zones: Each Availability Zone comprises one or more data centers. Availability Zones are tolerant to data center failures through redundancy and logical isolation of services.
Regions: Regions are typically located in different geographic areas and can be selected to keep data and applications close to users.
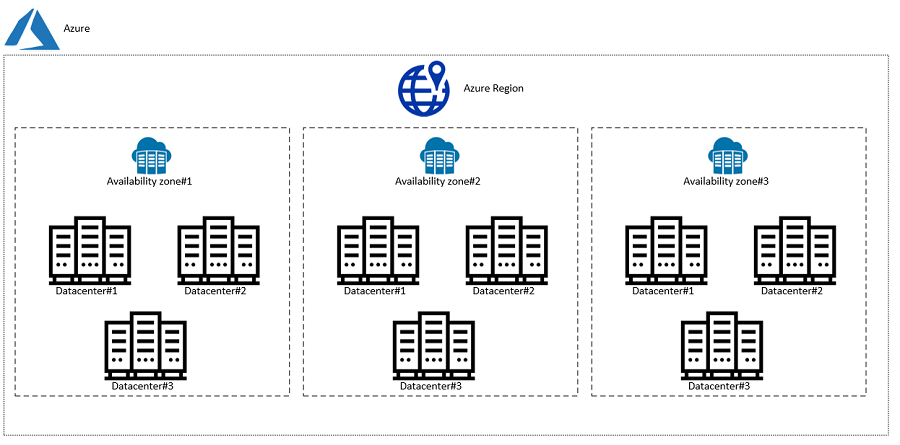
Source: https://www.unixarena.com/2020/08/what-is-the-availablity-zone-on-azure.html
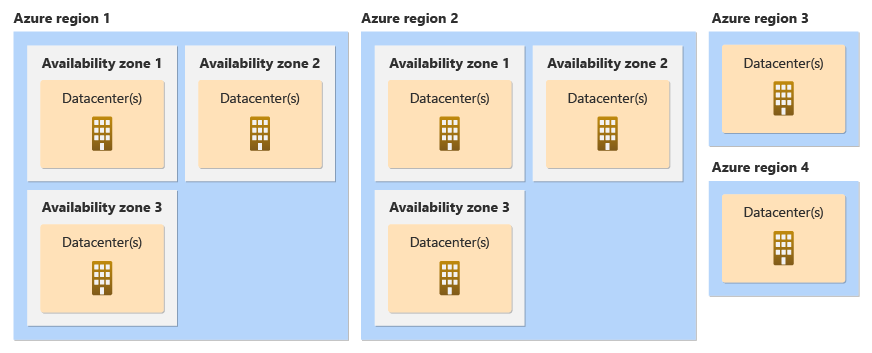
Source: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/reliability/availability-zones-overview?tabs=azure-cli
Paired Regions: Paired regions support certain types of multi-region deployment approaches.
Paired regions are physically separated by at least 300 miles, reducing the likelihood that a natural disaster or large-scale infrastructure failure would affect both regions.
Geo-Redundant Storage: Data replicated with GRS will be stored in the primary region and replicated in the secondary paired region.
Site Recovery: Azure Site Recovery services enable failover to the paired region in the event of a major outage.
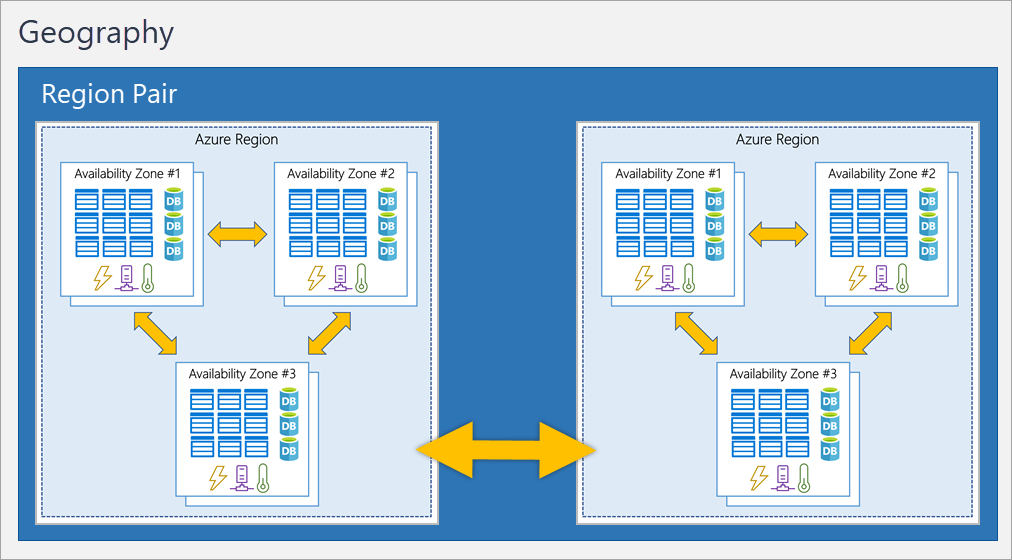
Source: https://i.stack.imgur.com/BwHct.png