[Avg. reading time: 6 minutes]
Concurrent vs. Parallel
Understanding the difference between concurrent and parallel programming is key when designing efficient, scalable applications — especially in distributed and multi-core systems.
Concurrent Programming
Concurrent programming is about managing multiple tasks at once, allowing them to make progress without necessarily executing at the same time.
- Tasks overlap in time.
- Focuses on task coordination, not simultaneous execution.
- Often used in systems that need to handle many events or users, like web servers or GUIs.
Key Traits
- Enables responsive programs (non-blocking)
- Utilizes a single core or limited resources efficiently
- Requires mechanisms like threads, coroutines, or async/await
Parallel Programming
Parallel programming is about executing multiple tasks simultaneously, typically to speed up computation.
- Tasks run at the same time, often on multiple cores.
- Focuses on performance and efficiency.
- Common in high-performance computing, such as scientific simulations or data processing.
Key Traits
- Requires multi-core CPUs or GPUs
- Ideal for data-heavy workloads
- Uses multithreading, multiprocessing, or vectorization
Analogy: Cooking in a Kitchen
Concurrent Programming
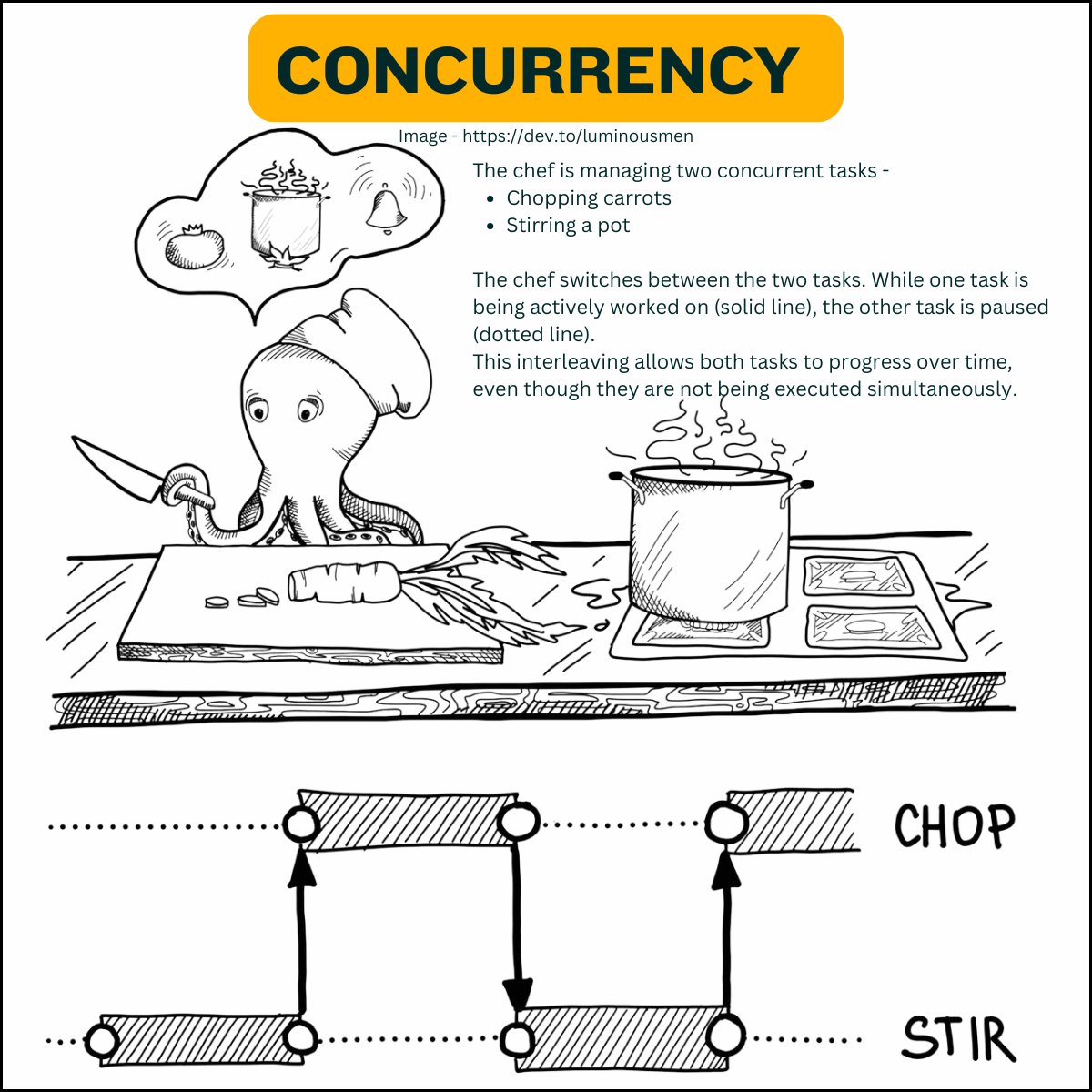
One chef is working on multiple dishes. While a pot is simmering, the chef chops vegetables for the next dish. Tasks overlap, but only one is actively running at a time.
Parallel Programming
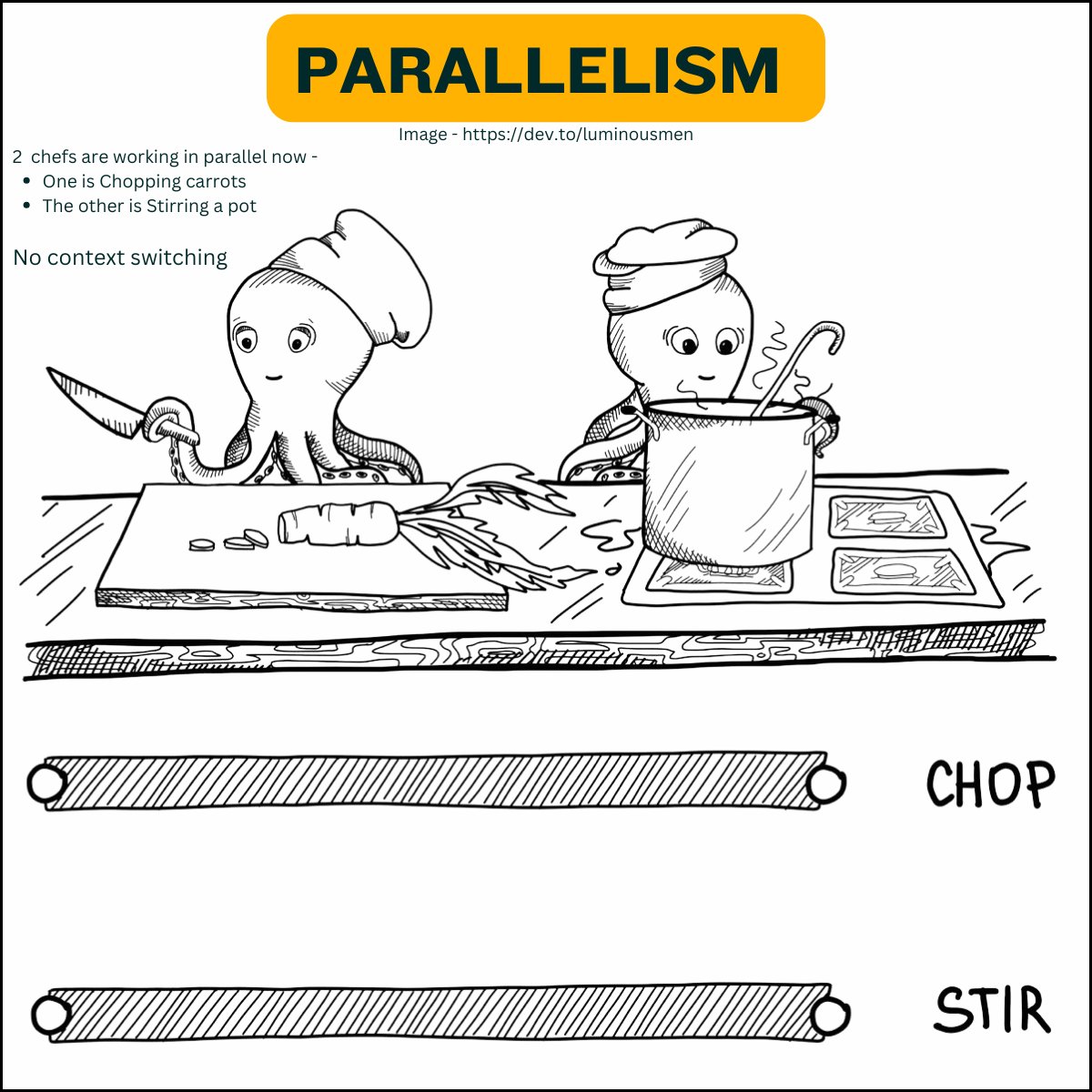
A team of chefs in a large kitchen, each cooking a different dish at the same time. Multiple dishes are actively being cooked simultaneously, speeding up the overall process.
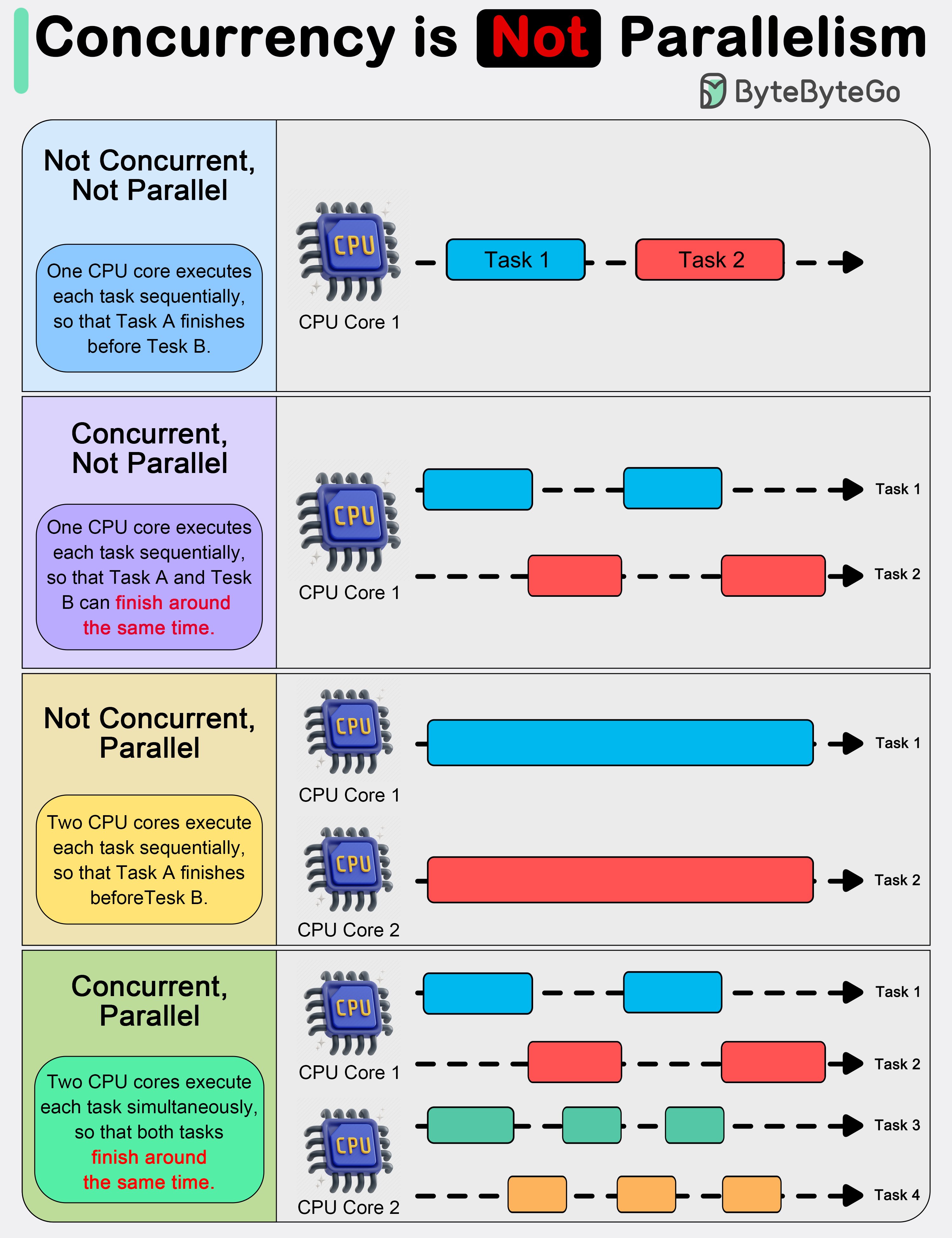
Summary Table
| Feature | Concurrent Programming | Parallel Programming |
|---|---|---|
| Task Timing | Tasks overlap, but not necessarily at once | Tasks run simultaneously |
| Focus | Managing multiple tasks efficiently | Improving performance through parallelism |
| Execution Context | Often single-core or logical thread | Multi-core, multi-threaded or GPU-based |
| Tools/Mechanisms | Threads, coroutines, async I/O | Threads, multiprocessing, SIMD, OpenMP |
| Example Use Case | Web servers, I/O-bound systems | Scientific computing, big data, simulations |