[Avg. reading time: 5 minutes]
Python Classes
Classes are templates used to define the properties and methods of objects in code. They can describe the kinds of data the class holds and how a programmer interacts with them.
Attributes - Properties
Methods - Action
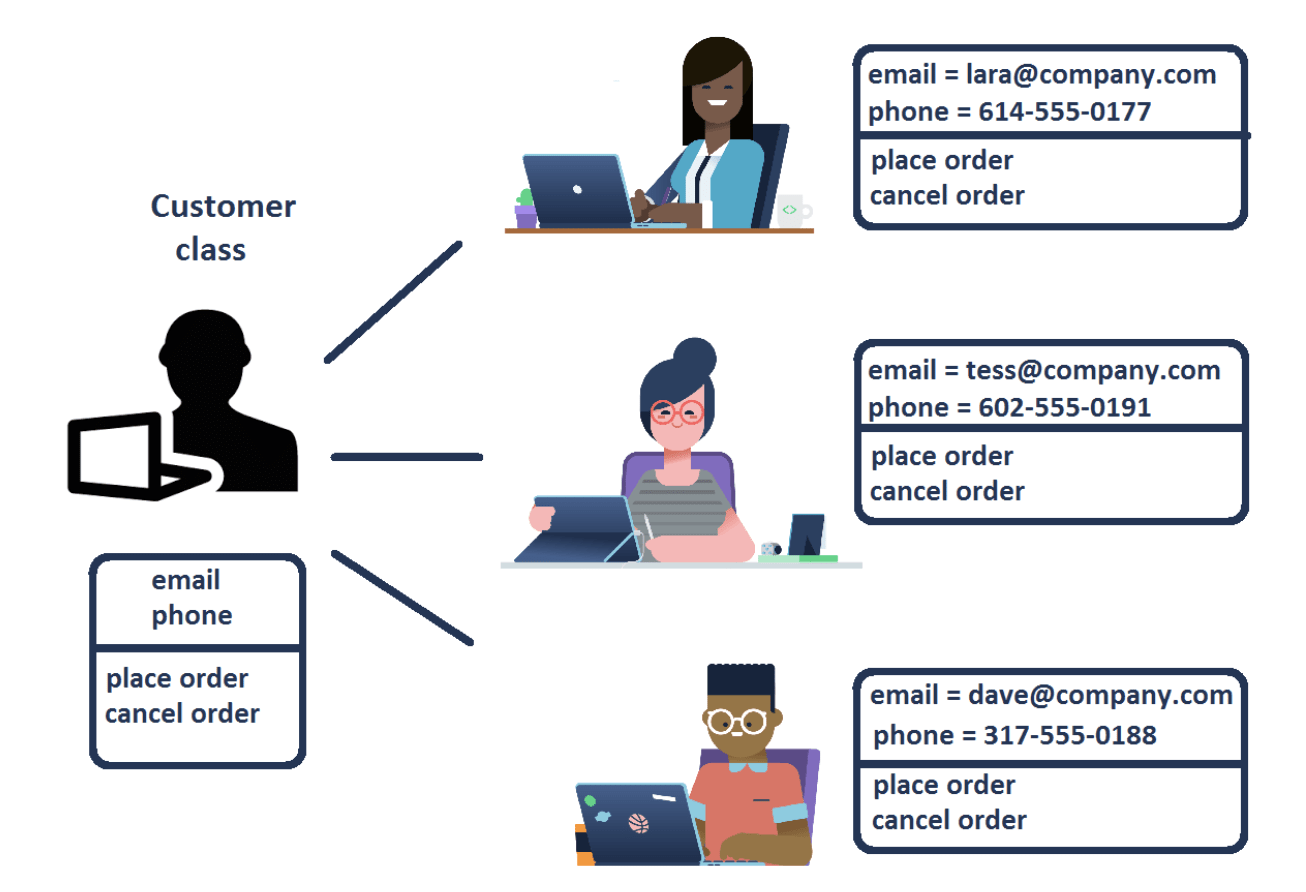
Img src: https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/python-classes
class Dog:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def bark(self):
print(f"{self.name} says woof! and its {self.age} years old")
my_dog = Dog("Buddy", 2)
my_dog.bark()
Class Definition: We start with the class keyword followed by Dog, the name of our class. This is the blueprint for creating Dog objects.
Constructor Method (__init__): This particular method is called automatically when a new Dog object is created. It initializes the object’s attributes. In this case, each Dog has a name and an age. The self parameter is a reference to the current instance of the class.
Attribute: self.name and self.age These are attributes of the class. These variables are associated with each class instance, holding the specific data.
Method: bark It is a method of the class. It’s a function that all Dog instances can perform. When called, it prints a message indicating that the dog is barking.
Python supports two types of methods within classes.
- StaticMethod
- InstanceMethod
Fork & Clone
git clone https://github.com/gchandra10/python_classes_demo.git